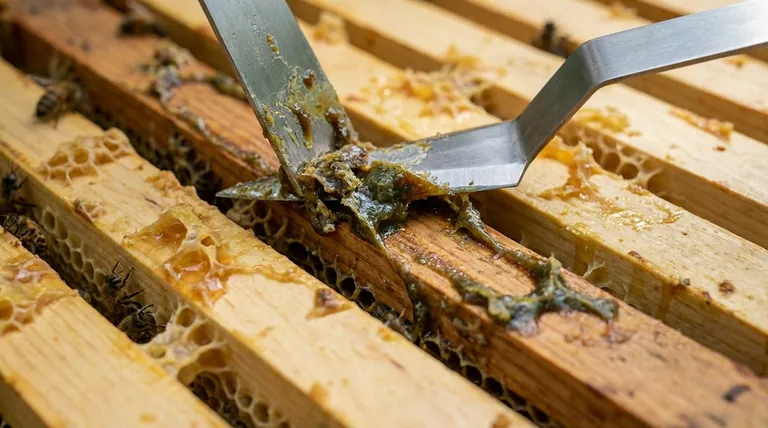
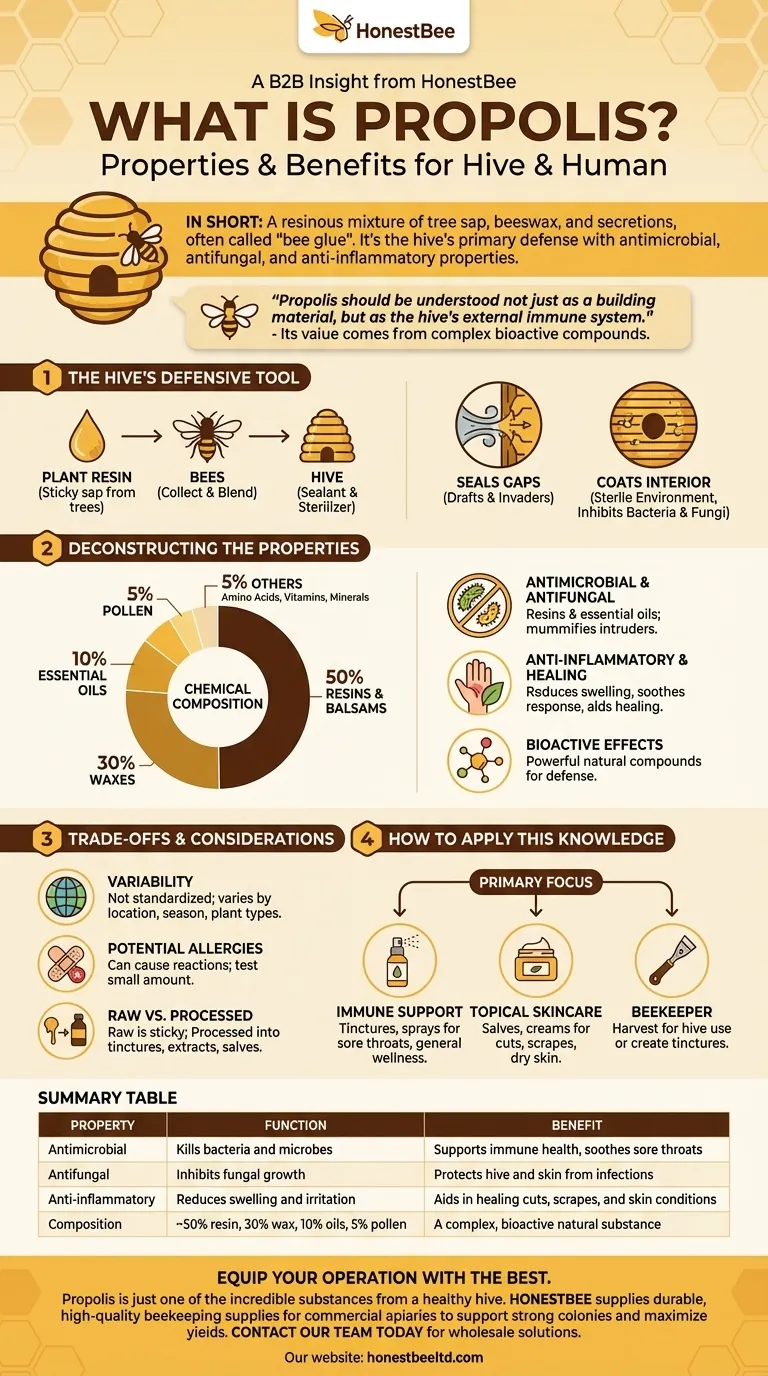
In short, propolis is a resinous mixture that honeybees produce by combining tree sap with their own beeswax and secretions. Often called "bee glue," this remarkable substance serves as the hive's primary defense mechanism, possessing powerful antimicrobial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties that humans have harnessed for medicinal purposes.
Propolis should be understood not just as a building material, but as the hive's external immune system. Its value to humans comes directly from the complex, bioactive compounds bees use to protect their colony from pathogens.

What is Propolis? The Hive's Defensive Tool
Propolis is a testament to the ingenuity of honeybees. It is a functional substance, created for a specific purpose, which is the source of its unique characteristics.
From Plant Resin to Hive Sealant
Bees are meticulous collectors. They gather resin—a sticky sap—from trees and other plants.
Back at the hive, they blend this resin with beeswax and their own enzymes. The result is a malleable, waxy, and incredibly sticky substance, typically greenish-brown in color.
The Role of Propolis Within the Hive
Bees use propolis as a universal construction and sterilization tool. Its primary function is to seal unwanted gaps and cracks in the hive, protecting the colony from drafts and invaders.
More importantly, they coat the entire interior surface of the hive with it. This creates a sterile environment, inhibiting the growth of bacteria and fungi and effectively acting as the colony's immune defense. It also helps ensure wooden frames slide smoothly during hive inspections.
Deconstructing the Properties of Propolis
The medicinal value of propolis is not folklore; it is a direct result of its complex chemical makeup. Understanding its composition is key to understanding its function.
The Chemical Composition
While its exact formula varies based on the local plant life, a typical sample of propolis contains a sophisticated blend of natural compounds.
On average, it is composed of approximately 50% resins and balsams, 30% waxes, 10% essential oils, and 5% pollen. The remainder includes various amino acids, vitamins, and minerals.
Bioactive Effects: Antimicrobial and Antifungal
The resins and essential oils are the primary sources of propolis's power. These compounds have been shown to have significant antibacterial, antimicrobial, and antifungal effects.
This is why bees use it to mummify intruders that are too large to remove, like a mouse, preventing the corpse from decomposing and spreading disease within the hive.
Anti-inflammatory and Healing Properties
The same bioactive compounds that fight microbes also help reduce inflammation. This has made propolis a key ingredient in traditional remedies for centuries.
Its use in healing salves, skin treatments, and remedies for sore throats or toothaches is directly linked to its ability to both kill pathogens and soothe an inflammatory response.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While propolis is a potent natural substance, it is essential to approach it with a clear understanding of its variability and potential limitations.
Variability is a Key Factor
Propolis is not a standardized product. Its chemical profile, color, and even its specific benefits can change dramatically depending on the geographic location, the season, and the types of trees and plants the bees visited.
Potential for Allergic Reactions
As with any bee product, including honey and royal jelly, propolis can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. It is always wise to test a small amount on your skin before using it more widely.
Raw vs. Processed Forms
In its raw state, propolis is a sticky, hard-to-manage gum. For human use, it is typically scraped from the hive and processed into a tincture (dissolved in alcohol), an extract, or infused into salves and creams to make it easier to apply.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Your interest in propolis should be guided by its natural function as a protective and healing agent.
- If your primary focus is immune support: Look for propolis tinctures or throat sprays, which leverage its antimicrobial properties to help soothe sore throats or support general wellness.
- If your primary focus is topical skincare: Consider salves or creams containing propolis extract for minor cuts, scrapes, or dry skin, utilizing its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
- If you are a beekeeper: You can harvest this valuable substance from your own hive frames and either return it to the hive or set it aside to create your own tinctures.
By understanding its origin and function, you can better appreciate propolis as a sophisticated, multipurpose tool developed by nature.
Summary Table:
| Property | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial | Kills bacteria and microbes | Supports immune health, soothes sore throats |
| Antifungal | Inhibits fungal growth | Protects the hive and skin from infections |
| Anti-inflammatory | Reduces swelling and irritation | Aids in healing cuts, scrapes, and skin conditions |
| Composition | ~50% resin, 30% wax, 10% oils, 5% pollen | A complex, bioactive natural substance |
Equip your operation with the best. Propolis is just one of the incredible substances produced by a healthy hive. For commercial apiaries and distributors, hive health is productivity. HONESTBEE supplies the durable, high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment you need to support strong colonies and maximize yields. From hive tools to protective gear, we provide wholesale-focused solutions for professionals. Contact our team today to discuss your needs and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Plastic Handle Single Row Artificial Fiber Bee Brush
- Premium 6-Cavity Bee and Floral Themed Silicone Soap Mold
- Boardman Entrance Bee Feeder Durable Galvanized Steel and Wood Construction for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE 6 Frame Three Use Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How do specialized consumables for collecting royal jelly and propolis help diversify apiary income? Boost Your Profits
- What are the advantages of using a rotary evaporator for propolis processing? Preserve Potency & Bioactive Integrity
- What role does a high-speed centrifuge play in the purification of propolis extracts? Achieve High-Purity Results
- Why is it necessary to use grinding equipment to pulverize frozen propolis? Optimize Your Extraction Yield Today
- What is the significance of using precision filter paper during the propolis extraction process? Master Purity Control
- How can propolis be harvested from a beehive? A Beekeeper's Guide to Efficient, Clean Collection
- What role do high-speed centrifuges play during the clarification stage of propolis extraction? Boost Efficiency & Purity
- Why are high-precision electronic balances essential for evaluating propolis yield? Data-Driven Bee Breed Comparison



















