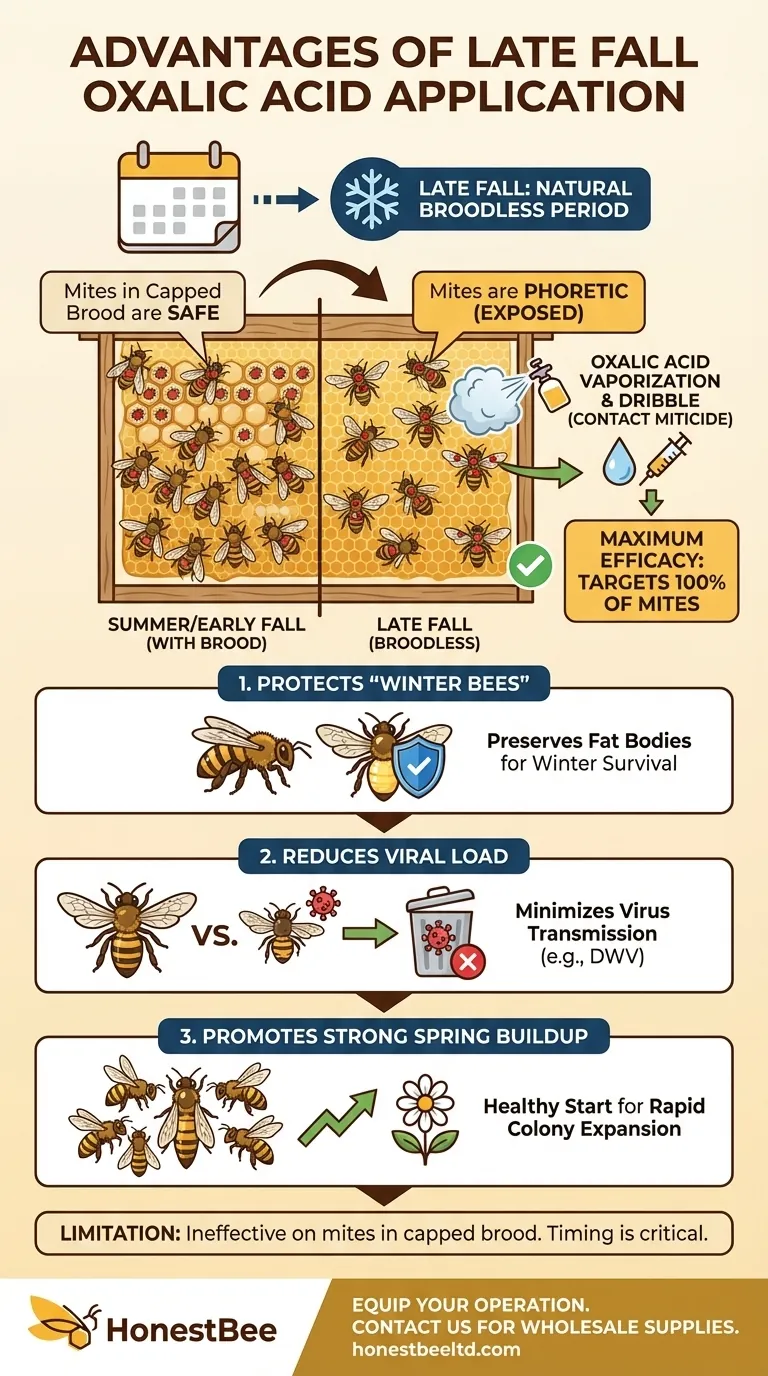
Applying oxalic acid in late fall is a highly effective tactic in an integrated pest management strategy against Varroa mites. This timing is specifically chosen because it aligns with a critical phase in both the bee colony's and the mite's life cycle. A successful application at this stage drastically reduces the mite population that the colony must carry through the winter, directly boosting its chances of survival and promoting a stronger start in the spring.
The strategic advantage of a late-fall oxalic acid treatment is not about the chemical itself, but its timing. By applying it during a naturally occurring "broodless" period, you target the entire Varroa mite population at its most vulnerable, achieving maximum impact with a single, well-placed intervention.
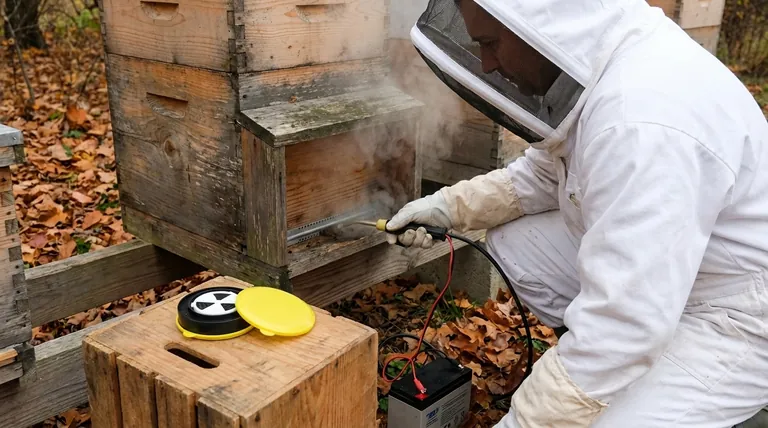

The Science Behind the Timing: Varroa and the Brood Cycle
To understand the power of a late-fall treatment, you must first understand the relationship between the Varroa mite's life cycle and the colony's brood cycle.
Understanding Phoretic Mites
The Varroa destructor mite exists in two phases. The reproductive phase occurs hidden from view, under the capped cells of developing bee pupae.
The second phase is the phoretic stage. During this time, mites are physically attached to the bodies of adult bees, feeding on their fat body tissue and transmitting viruses. It is only in this exposed, phoretic stage that they are vulnerable to an oxalic acid treatment.
The Natural Late Fall Brood Break
As temperatures drop and nectar sources disappear in the fall, the queen bee naturally ceases or dramatically reduces her egg-laying. This results in a period where the hive has very little or no sealed brood.
This "brood break" is a critical window of opportunity. With no brood cells to hide in, virtually the entire mite population within the hive is forced into the phoretic stage, riding on adult bees.
Why This Window is So Effective
Oxalic acid treatments, whether by vaporization or dribble method, are "contact" miticides. They only kill the mites they physically touch on the adult bees.
By treating during the broodless period, you are not just killing a fraction of the mites; you are targeting nearly 100% of the mite population in a single application. This is the highest level of efficacy you can achieve with this treatment.
Maximizing Impact for Winter Survival
Lowering the mite count is always the goal, but doing so just before winter provides unique and powerful benefits for the colony.
Protecting the "Winter Bees"
Bees born in the late fall are physiologically different. These "winter bees" have more developed fat bodies and are engineered to live for several months, sustaining the cluster through the winter.
Varroa mites preferentially feed on these fat bodies, weakening the bees and reducing their lifespan. A pre-winter treatment protects this critical generation of bees, ensuring the cluster has the strength and longevity to survive until spring.
Reducing the Pre-Winter Viral Load
Mites are potent vectors for a host of deadly viruses, such as Deformed Wing Virus (DWV). A high mite load going into winter means a high viral load as well.
Eliminating the mites just before the colony clusters for winter effectively cleanses the hive of these vectors, reducing virus transmission and giving the bees a healthier start to their long confinement.
Paving the Way for a Strong Spring
A colony that emerges from winter with a low mite population can dedicate its resources to rapid expansion and foraging.
Conversely, a colony that struggles with a high winter mite load will emerge weak, with a smaller population and a higher viral presence. This often leads to a slow, difficult spring buildup or even colony collapse in early spring.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective when used correctly, oxalic acid is not a silver bullet. Understanding its limitations is crucial for responsible use.
Ineffectiveness on Mites in Capped Brood
The single most important limitation is that oxalic acid does not penetrate the wax cappings of brood cells.
If you treat a colony that has a significant amount of brood, all the mites reproducing within those cells will be completely unaffected. This is why confirming a true broodless state is paramount for efficacy.
Risk of Mis-timing
Applying the treatment too early, while the queen is still laying, will result in poor mite control. Applying it too late, when the colony is tightly clustered in deep cold, can make it difficult for the treatment (especially vapor) to distribute evenly.
Method of Application Matters
The two primary methods, vaporization and dribble, have their own protocols. Vaporization offers excellent distribution but requires specific safety equipment for the beekeeper. The dribble method is simpler but can be harder on the bees if temperatures are too cold or the dose is incorrect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Integrating a late-fall oxalic acid treatment into your Integrated Pest Management (IPM) plan requires understanding your specific conditions.
- If your primary focus is maximum efficacy: Wait to apply oxalic acid until the colony is confirmed to be broodless, which is often 3-4 weeks after the first consistent hard frosts.
- If you manage bees in a climate with no true brood break: Recognize that a single oxalic acid treatment will be insufficient and must be combined with other mite control methods that work in the presence of brood.
- If your primary focus is long-term colony health: Use the late fall treatment as a critical "clean-up" step after your main summer or early fall mite control, ensuring the colony enters winter with the lowest possible mite load.
Ultimately, a well-timed oxalic acid application is a cornerstone of proactive beekeeping, directly empowering your colonies to survive the winter and thrive the following year.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Targets 100% of Mites | Applied during the natural broodless period, mites have nowhere to hide, ensuring maximum contact and efficacy. |
| Protects Winter Bees | Reduces viral load and protects the fat bodies of long-lived winter bees, crucial for colony survival. |
| Promotes Strong Spring Buildup | A healthy, low-mite colony can dedicate energy to rapid expansion instead of fighting disease. |
| Single, Efficient Intervention | Achieves high mite knockdown with one well-timed application, simplifying fall management. |
Equip your operation for effective Varroa control. A successful late-fall treatment starts with the right equipment. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with high-quality, wholesale-focused supplies, including oxalic acid vaporizers and dribble kits. Ensure your colonies enter winter strong and healthy—contact our team today to discuss your needs and bulk pricing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Adjustable Formic and Acetic Acid Dispenser for Bee Mite Treatment
- Professional Bamboo Queen Isolation Cage
- Black Plastic Beetle Barn Hive Beetle Trap for Beehives
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Professional Grade Foldable Beehive Handles
People Also Ask
- What are the technical requirements for Varroa mite treatments? Essential Strategies for Colony Health
- What are the common technical treatments used for Varroa mite control in the spring? Optimize Colony Health Today
- Why is a high-precision larva and pupa extraction process required when analyzing Varroa mite reproductive success?
- What unique benefits do formic acid evaporators offer for mite control? The Only Safe Solution During Honey Flow
- How should Varroa mite treatments be integrated into the spring beekeeping schedule? Expert April-May Timing Guide



















