At its core, the capping and sealing process is the final, critical step in a filling machine's operation, designed to guarantee product integrity. This process serves two primary functions: it physically contains the product by preventing leaks and it protects the product's quality by creating a barrier against external contaminants.
Capping and sealing are not merely about closing a container. They are a strategic engineering decision that directly impacts product safety, shelf life, and brand reputation, acting as the ultimate gatekeeper between your product and the outside world.
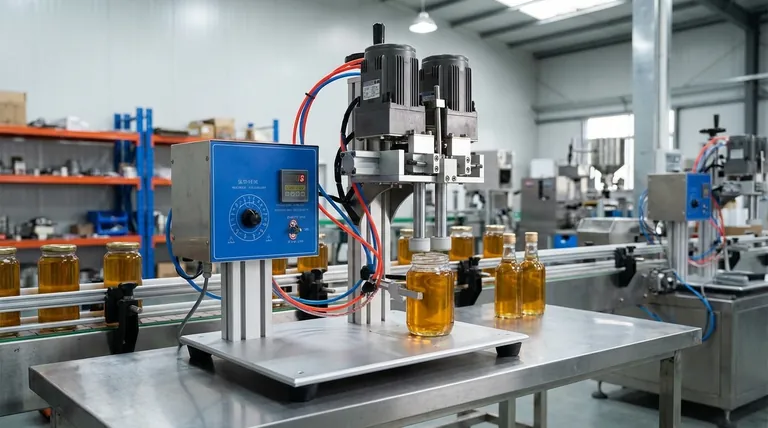

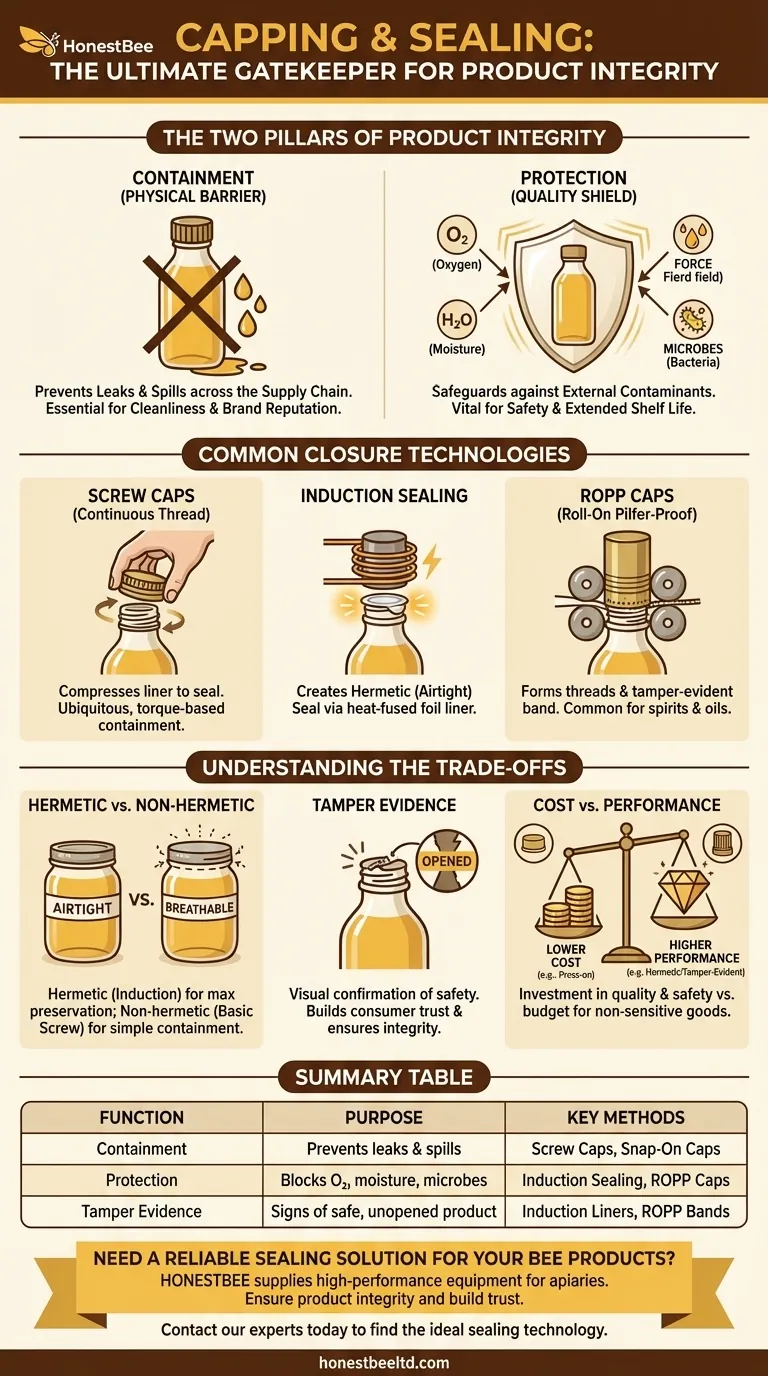
The Two Pillars of Product Integrity
The purpose of any closure system can be broken down into two fundamental responsibilities: containment and protection. While related, they address different risks in the product's lifecycle.
Containment: The Physical Barrier
The most obvious function of a cap is containment. It creates a physical barrier to stop the product from spilling or leaking out of its container.
This is essential not just for the end consumer, but throughout the entire supply chain. A failed seal leads to lost product, damaged secondary packaging, and costly cleanups during shipping and storage. On a retail shelf, a leaky container is unsellable and reflects poorly on the brand.
Protection: The Quality Shield
Beyond simple containment, the seal acts as a protective shield for the product inside. It safeguards the contents from a range of external factors that can degrade quality and shorten shelf life.
This includes preventing the ingress of oxygen, moisture, microorganisms, and other environmental contaminants. For many food, beverage, and pharmaceutical products, this protection is non-negotiable for ensuring safety and efficacy.
Exploring Common Closure Technologies
The method used for capping and sealing depends entirely on the product, the container type, and the required level of protection.
Screw Caps (Continuous Thread)
This is the most ubiquitous closure type, found on everything from water bottles to jars of sauce. The cap is tightened to a specific torque value, compressing a liner inside the cap against the rim of the container to form a seal.
Induction Sealing
For a truly airtight, or hermetic seal, induction sealing is the industry standard. A multi-layer liner is placed inside the cap, with one layer being aluminum foil. After capping, the container passes through an electromagnetic field, which heats the foil and melts a polymer layer, fusing it to the container's rim.
ROPP Caps (Roll-On Pilfer-Proof)
Commonly used for wine and spirits, ROPP caps are unthreaded aluminum shells. The capping machine presses the cap onto the bottle and uses rollers to form the threads directly onto the bottle's neck. This process simultaneously creates a tight seal and a perforated, tamper-evident band at the base.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right closure system involves balancing protection, cost, and consumer experience. There is no single "best" method; there is only the best method for a specific application.
Hermetic vs. Non-Hermetic Seals
The most critical distinction is between a hermetic seal and a non-hermetic one. An induction seal is hermetic—it is impermeable to air and gas exchange, which is vital for preserving freshness in products like coffee or cooking oil. A basic screw cap without an induction liner is non-hermetic; it provides good containment but offers minimal protection against oxygen or moisture ingress over time.
Tamper Evidence as a Critical Feature
Many sealing methods are designed to provide clear tamper evidence. ROPP caps and induction seals must be broken to open the container, giving consumers a clear, visual confirmation that the product has not been opened since it left the factory. This is a crucial feature for building consumer trust and ensuring safety.
Cost vs. Required Performance
A simple press-on cap is far less expensive than a multi-part induction-ready screw cap. The decision comes down to a risk-benefit analysis. For non-sensitive industrial products, a basic cap may be sufficient. For high-value pharmaceuticals or oxygen-sensitive foods, the added cost of a hermetic, tamper-evident seal is a necessary investment in product quality and safety.
Matching the Method to Your Product's Needs
Your choice of capping and sealing technology should be driven by the specific demands of your product and market.
- If your primary focus is maximum shelf life and safety (foods, beverages, pharma): An induction seal is the definitive choice for creating a hermetic, tamper-evident barrier.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective containment for non-sensitive goods (dry goods, some chemicals): A standard continuous thread screw cap or snap-on cap offers reliable performance.
- If your primary focus is tamper evidence and a premium feel (spirits, high-value oils): A ROPP capping system provides an excellent seal while clearly demonstrating product integrity.
Ultimately, the right closure strategy transforms a simple package into a secure, reliable, and trustworthy product.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose | Key Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Containment | Prevents leaks and spills during shipping and storage. | Screw Caps, Snap-On Caps |
| Protection | Blocks oxygen, moisture, and microbes to preserve quality. | Induction Sealing, ROPP Caps |
| Tamper Evidence | Provides a clear sign the product is safe and unopened. | Induction Liners, ROPP Bands |
Need a reliable sealing solution for your products?
HONESTBEE supplies high-performance capping and sealing equipment to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors. We understand that protecting the quality of your honey, propolis, and other bee products is non-negotiable. Our solutions help you achieve the perfect seal to ensure product integrity, extend shelf life, and build consumer trust.
Contact our experts today to find the ideal sealing technology for your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Semi-Automatic Pneumatic Bottle Capping Machine by HONESTBEE
- Automatic Honey Frame Uncapper Machine for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE 24 Head Rotary Bottle Washing Machine
- Lightweight Plastic Uncapping Roller with Tines
- Professional Stainless Steel Uncapping Fork with Wooden Handle
People Also Ask
- How does a bottle capping machine work? Unlock Efficient, Consistent Sealing for Your Production Line
- What is the purpose of a bottle capping machine? Boost Efficiency and Ensure Product Integrity
- What is a bottle cap sealing machine? The Key to Automated, Tamper-Evident Packaging
- What are the categories of bottle capping machines? Choose the Right Automation for Your Line
- What is the role of a capping scratcher in the uncapping process? The Essential Tool for Maximum Honey Yield



















