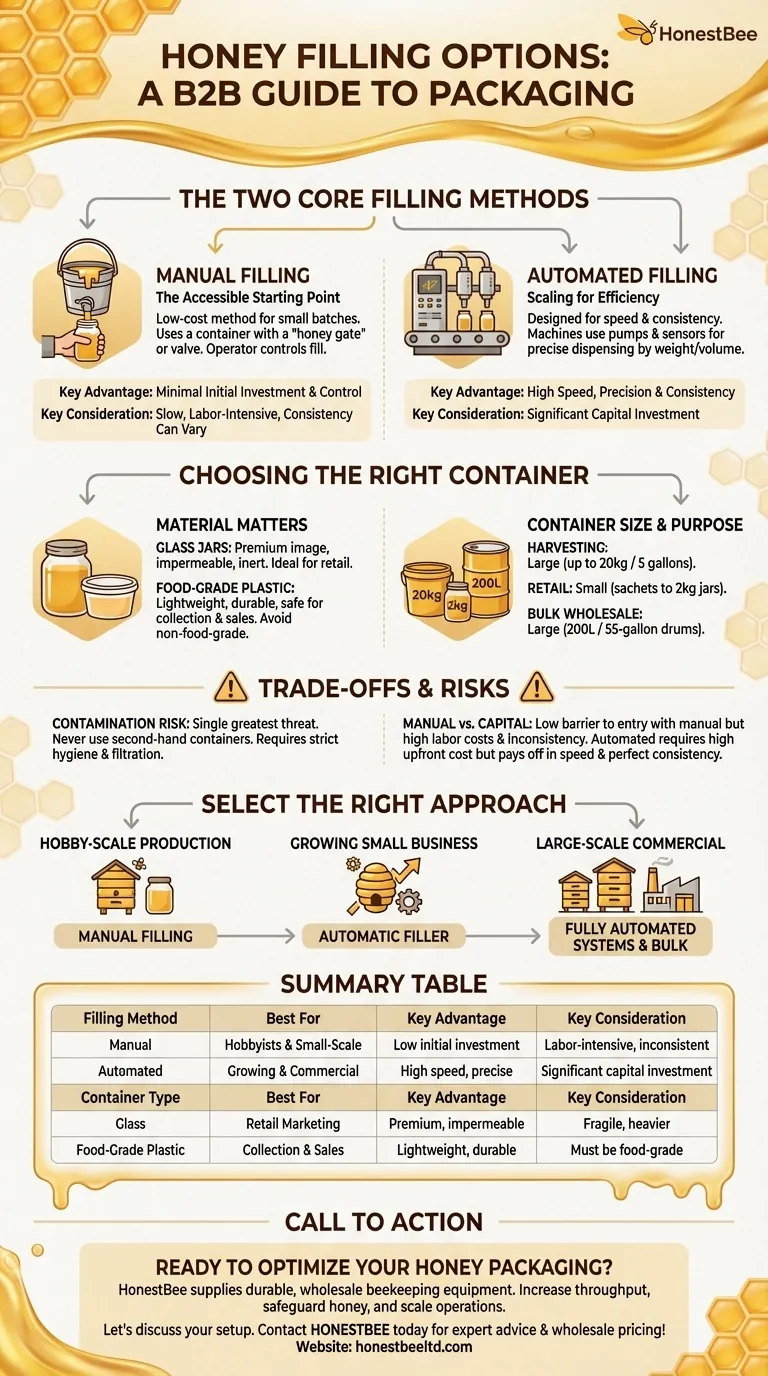
When it comes to packaging honey, you have two primary methods: filling containers manually or using an automated filling machine. Manual filling is the traditional, low-cost approach suitable for smaller batches, while automated fillers provide speed, precision, and consistency for larger-scale operations by dispensing honey based on a pre-set weight or volume.
The choice between manual and automated honey filling hinges on your production volume and budget. However, regardless of the method, the non-negotiable factors for a quality product are the exclusive use of food-grade containers and a strict commitment to hygiene.

The Two Core Filling Methods
Understanding the mechanics and ideal use case for each filling method is the first step in creating an efficient packaging process.
Manual Filling: The Accessible Starting Point
Manual filling is the most common method for hobbyists and small-scale producers. It typically involves using a container, like a food-grade bucket, equipped with a "honey gate" or valve at the bottom.
This approach requires minimal initial investment and offers complete control. The operator opens the gate to fill each jar and closes it when the desired level is reached, often weighing each jar individually to ensure accuracy.
Automated Filling: Scaling for Efficiency
Automated fillers are designed for speed and consistency in commercial settings. These machines use pumps and sensors to dispense a precise amount of honey into each container.
Operators can set the machine to a specific weight, and the filler handles the rest, dramatically increasing throughput and reducing labor. This ensures every container is filled uniformly, which is critical for professional sales.
Choosing the Right Container: A Critical Decision
The container is more than just packaging; it's essential for preserving the honey's quality and ensuring food safety.
Material Matters: Glass vs. Food-Grade Plastic
Glass jars with tight-fitting lids are considered an ideal choice for storing and marketing honey. They are inert, impermeable, and present a premium image to consumers.
Food-grade plastic containers are also a popular and safe option. They are lighter and less fragile than glass, making them excellent for both collection and final sales. It is critical to avoid non-food-grade plastics or metals, as they can react with the honey and cause oxidation, altering its flavor and quality.
Matching Container Size to Your Purpose
The right container size depends entirely on its intended use.
For harvesting and processing, larger containers up to 20 kg (approx. 5 gallons) are practical for collecting extracted honey. For retail marketing, smaller containers ranging from 2 kg down to small jars or plastic sachets are most common. For bulk wholesale, large 200-liter (55-gallon) drums are the industry standard.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
A successful bottling process involves mitigating risks and making informed choices between cost and efficiency.
The High Cost of Contamination
Contamination is the single greatest threat to your product. Never use second-hand containers, as they can introduce bacteria or foreign residues.
To ensure purity, consider implementing a filtration system to remove small impurities like wax particles. Additionally, all equipment, whether a simple bottling bucket or a complex filling machine, must be thoroughly cleaned and sanitized before use.
Manual Labor vs. Capital Investment
The central trade-off is between labor and equipment cost. Manual filling has a very low barrier to entry but is slow, labor-intensive, and can lead to inconsistent fill levels.
Automated systems require a significant capital investment upfront but pay for themselves over time through dramatically increased speed, reduced labor costs, and perfect consistency.
How to Select the Right Approach
Your choice should directly support your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is hobby-scale production: Manual filling with a bottling bucket is the most practical and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is growing a small business: An automatic filler is a logical investment to increase efficiency and ensure professional, consistent packaging.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial operation: Fully automated systems and bulk containers are essential for achieving the volume and profitability required.
By carefully matching your filling method and container choice to your specific scale, you can package your honey efficiently while safeguarding its quality and value.
Summary Table:
| Filling Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Filling | Hobbyists & Small-Scale Producers | Low initial investment | Labor-intensive, potential for inconsistency |
| Automated Filling | Growing Businesses & Commercial Apiaries | High speed and precise consistency | Requires significant capital investment |
| Container Type | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Consideration |
| Glass Jars | Retail Marketing | Premium image, impermeable | Fragile, heavier |
| Food-Grade Plastic | Collection & Sales | Lightweight, durable | Must be food-grade to prevent contamination |
Ready to Optimize Your Honey Packaging?
As a commercial apiary or beekeeping equipment distributor, your efficiency and product quality are paramount. HONESTBEE supplies the durable, wholesale-focused beekeeping supplies and equipment you need to succeed.
- Increase Your Throughput: Our automated filling solutions ensure precise, consistent fills for a professional product.
- Safeguard Your Honey: We provide food-grade containers and equipment designed to prevent contamination.
- Scale Your Operations: From bottling buckets for smaller batches to high-volume automated systems, we have solutions for every stage of growth.
Let's discuss the best packaging setup for your business. Contact HONESTBEE today for expert advice and wholesale pricing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Honey Concentrating and Filtering Dehumidifier Machine 2T Capacity for Honey
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- Electric Honey Press Machine for Squeezing Honey Comb Press Equipment
- Stainless Steel Triangle Support Honey Strainer and Filters
- Electric 8 Frame Honey Spinner Extractor Equipment for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between fluid ounces and net weight ounces when measuring honey? Master Honey Bottling Precision
- What is the main goal of the filling machine process? Ensure Precision & Integrity for Your Products
- What are the technical advantages of using industrial honey filling machines? Boost Precision and Safety
- How should one troubleshoot display errors on a filling machine's control panel? Expert Solutions for Rapid Recovery
- What is the role of industrial-grade honey filling machines in standardized production? Expert Guide to PDO/PGI Quality
- What is the recommended weekly maintenance for a honey stick machine? Ensure Peak Performance and Longevity
- What is the economic value of using commercial automated honey filling equipment? Maximize Profit Despite Low Yields
- What is the primary value of automated Honey-filling Machines? Scale Your Apiary with Precision and Hygiene



















