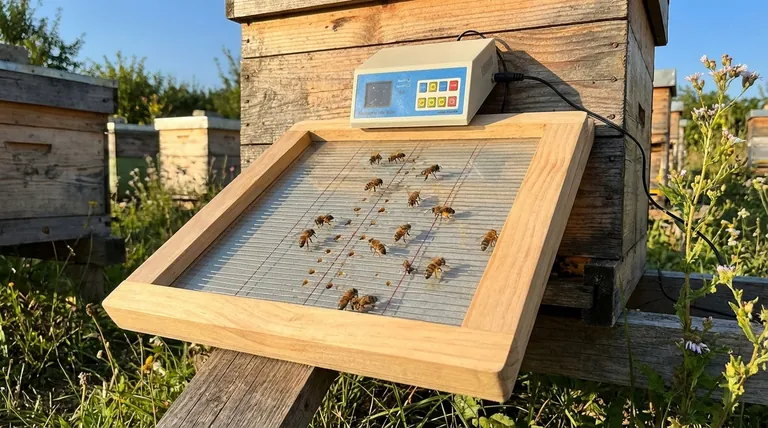
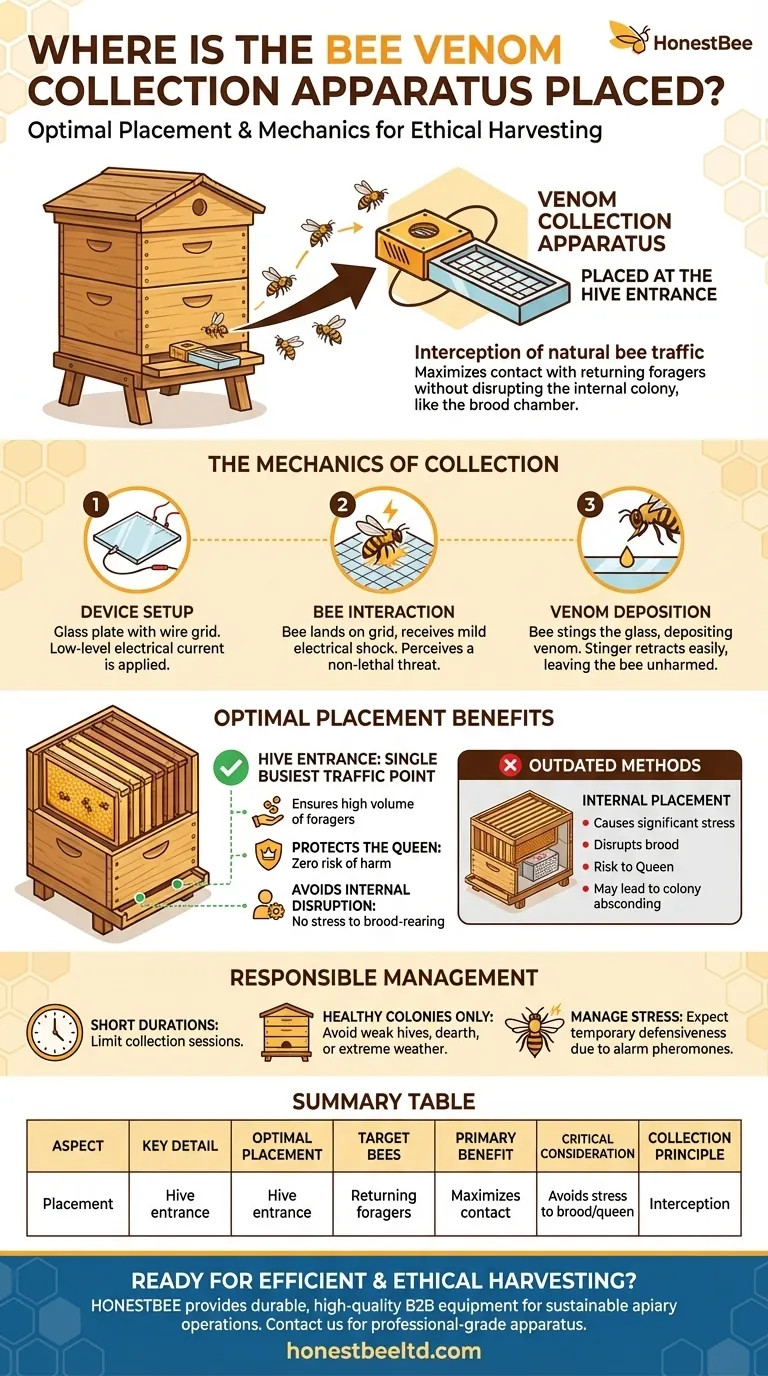
To collect bee venom, the collection apparatus, often a glass plate with an electrical grid, is placed at the entrance of the beehive. This strategic placement ensures that returning forager bees must walk across the device to enter the hive, maximizing contact and venom collection.
The core principle of bee venom collection is interception. Placing the collector at the hive entrance forces interaction with the maximum number of bees without disrupting the internal colony structure, like the brood chamber.

The Mechanics of Venom Collection at the Hive Entrance
Placing the collection device at the hive entrance is the universally accepted and most effective method. This location leverages the natural daily traffic of the colony's foragers.
How the Device Works
A typical venom collector consists of a glass plate covered by a wire grid. A low-level electrical current is passed through this grid.
When a bee lands and walks on the grid, it receives a mild electrical shock. This stimulus is not lethal but is enough to make the bee perceive a threat.
The Bee's Defensive Response
The bee's natural defensive instinct is to sting the perceived threat. It extends its stinger and deposits a droplet of venom onto the glass plate beneath the wires.
Crucially, the bee's stinger does not get stuck in the hard glass surface. This allows the bee to retract its stinger and fly away unharmed, unlike when it stings a mammal.
Why the Entrance is the Optimal Location
The hive entrance is the single busiest point of traffic for a colony. Placing the collector here ensures a high volume of bees—primarily the older, experienced foragers—will interact with the device.
This method avoids internal disruption. Placing a foreign object inside the brood chamber, as some outdated sources might suggest, would cause significant stress, disrupt brood-rearing, and could lead to the queen's death or the colony absconding.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
While effective, venom collection is an invasive process that requires careful management to minimize harm to the colony.
Stress and Aggression
The electrical stimulation agitates the colony. The bees release alarm pheromones, which can make the entire hive more defensive and aggressive for a period.
For this reason, collectors should only be operated for short durations. Continuous operation would put unsustainable stress on the colony.
Colony Health is Paramount
Venom collection should only be performed on strong, healthy, and populous colonies. A weak colony may not be able to withstand the stress and loss of energy associated with the collection process.
It is also critical to avoid collecting during periods of nectar dearth or extreme weather, as the colony needs all its resources focused on survival.
Protecting the Queen
The queen bee never leaves the hive except for her initial mating flights. By placing the collector at the entrance, there is virtually zero risk of harming the queen, which is essential for the colony's long-term survival.
Applying This to Your Apiary
The correct placement and responsible management of the venom collector are non-negotiable for ethical and effective harvesting.
- For maximum collection efficiency: Place the venom collector directly at the main entrance of a strong, populous hive on a warm, active day.
- To ensure colony safety: Never place the device inside the brood chamber or any other internal part of the hive.
- For sustainable beekeeping: Limit collection sessions to short periods and give the colony ample recovery time between collections.
Proper placement at the hive entrance is the key to successfully harvesting bee venom while preserving the health and integrity of the colony.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Optimal Placement | Hive entrance |
| Target Bees | Returning foragers |
| Primary Benefit | Maximizes contact without internal disruption |
| Critical Consideration | Avoids stress to the brood chamber and queen |
| Collection Principle | Interception of natural bee traffic |
Ready to implement efficient and ethical venom collection in your apiary?
As a trusted supplier for commercial apiaries and distributors, HONESTBEE provides the durable, high-quality equipment you need for sustainable operations. Our wholesale-focused approach ensures you get reliable tools that protect your colony's health while maximizing your yield.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your beekeeping equipment needs and secure your supply of professional-grade venom collection apparatus.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Full Set Beekeeping Electronic Bee Venom Collector Machine Device for Bee Venom Collecting
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Beehive Handle and Frame Rest Cutting Machine: Your Specialized Hive Machine
- Plastic Hand Crank 2 Frame Honey Extractor Low Price
- 6 Frame Manual Stainless Steel Honey Extractor Beekeeping Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the function of an electronic pulse bee venom collector? Boost Revenue Without Harming Your Colony
- How does an electronic bee venom collector facilitate the harvesting of apitoxin? Enhance Yield and Purity Safely
- What is the primary function of an electric stimulus bee venom collection device? Optimize Your Venom Yield Safely
- What is the role of specialized bee venom extraction equipment? Secure High-Purity Bioactive Substances Sustainably
- What is the working principle and advantage of a pulse generator type bee venom collector? Harvest High-Purity Venom



















