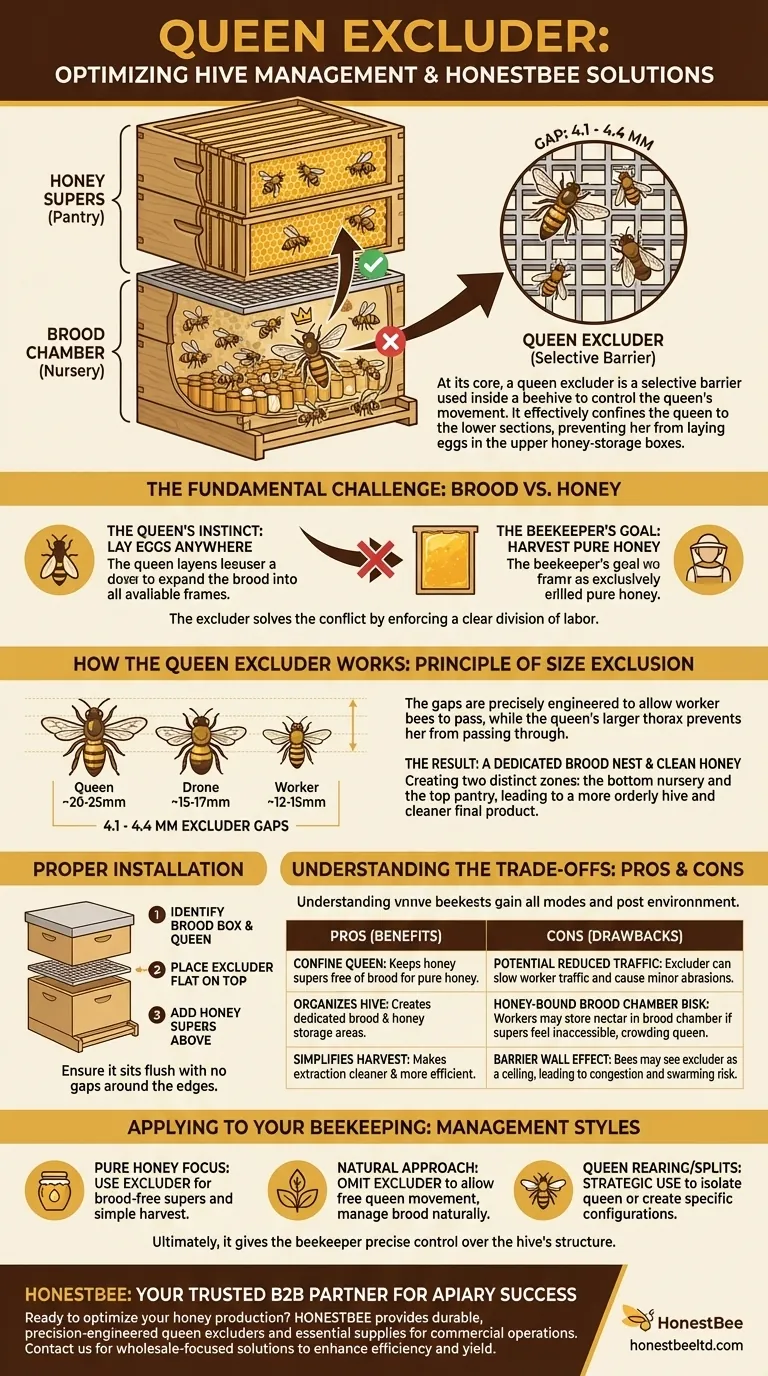
At its core, a queen excluder is a selective barrier used inside a beehive to control the queen's movement. It is a simple grid, made of metal or plastic, with openings large enough for worker bees to pass through but too small for the larger queen and drones. This design effectively confines the queen to the lower sections of the hive, known as the brood chamber, preventing her from laying eggs in the upper honey-storage boxes, called honey supers.
A queen excluder is a management tool that separates the queen's egg-laying area from the colony's honey storage area. This ensures honey supers remain free of brood, which simplifies honey harvesting and maintains its purity.

The Fundamental Challenge: Brood vs. Honey
To understand the value of an excluder, you must first understand the conflicting goals of the bees and the beekeeper.
The Queen's Instinct to Expand
A healthy queen bee has one primary job: to lay eggs. She will seek out empty cells anywhere in the hive to expand the colony's population. Without intervention, she will happily lay eggs in the frames meant for honey storage.
The Beekeeper's Goal of Pure Honey
The beekeeper's goal is to harvest frames filled exclusively with honey. When frames contain a mix of honey, pollen, eggs, and larvae (brood), the extraction process becomes messy and difficult, and the final quality of the honey can be compromised.
How the Queen Excluder Solves the Problem
The queen excluder is a simple, physical solution to this conflict of interest. It enforces a clear division of labor within the hive.
The Principle of Size Exclusion
The device works by exploiting the size difference between bees. The gaps in the excluder are precisely engineered, typically between 4.1 and 4.4 millimeters. This is wide enough for smaller worker bees to squeeze through to deposit nectar in the honey supers.
However, the queen's larger thorax prevents her from passing through the grid. Drones, the male bees, are also too large to pass and are kept out of the honey supers.
The Result: A Dedicated Brood Nest
By placing the excluder between the brood chamber and the honey supers, the beekeeper creates two distinct zones. The bottom of the hive becomes the nursery, and the top becomes the pantry. This organization leads to a more orderly hive and a much cleaner final product for the beekeeper.
Proper Installation
Installing an excluder is straightforward. After identifying which hive body contains the queen and the brood, you simply place the excluder flat on top of that box. Ensure it sits flush with no gaps around the edges. Any honey supers are then placed directly on top of the excluder.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, the use of a queen excluder is a subject of debate among beekeepers, and it's important to understand the potential downsides.
Potential for Reduced Hive Traffic
The excluder is a physical barrier. Some beekeepers argue that forcing worker bees to constantly squeeze through the grid can slow them down, potentially reducing the overall rate of honey production. It can also cause minor abrasion to their wings and bodies over time.
Risk of a "Honey-Bound" Brood Chamber
If the honey flow is particularly strong, workers may be reluctant to pass through the excluder. Instead, they might begin storing nectar in empty cells within the brood chamber. This can "crowd out" the queen, leaving her with no space to lay eggs and potentially slowing the colony's growth.
Creation of a Barrier Wall
Bees sometimes see the excluder as a ceiling and may be hesitant to work in the supers above it. This can lead to increased congestion and a higher likelihood of the colony deciding to swarm.
How to Apply This to Your Beekeeping
Deciding whether to use a queen excluder depends entirely on your management style and primary goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing clean honey production: A queen excluder is an invaluable tool for ensuring your honey supers are free of brood, making for a simple and efficient harvest.
- If your primary focus is a more natural, hands-off approach: You may choose to omit the excluder and allow the queen to roam freely, managing the brood nest through other methods.
- If your primary focus is raising new queens or managing hive splits: An excluder can be used strategically to isolate a queen or create specific hive configurations, such as a two-queen system.
Ultimately, the queen excluder is a tool that gives the beekeeper precise control over the hive's internal structure.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Potential Drawback |
|---|---|---|
| Confines Queen | Keeps honey supers free of brood for pure honey. | Can slightly slow worker bee traffic. |
| Organizes Hive | Creates dedicated brood and honey storage areas. | Risk of a "honey-bound" brood chamber. |
| Simplifies Harvest | Makes honey extraction cleaner and more efficient. | May be seen as a barrier, increasing swarming risk. |
Ready to optimize your honey production with reliable equipment? As a trusted supplier for commercial apiaries and distributors, HONESTBEE provides the durable, precision-engineered queen excluders and other essential supplies your operation needs to succeed. Let's discuss how our wholesale-focused solutions can enhance your efficiency and yield. Contact HONESTBEE today for a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Performance Plastic Queen Excluder for Beekeeping and Apiary Management
- Professional Plastic Queen Excluder for Modern Beekeeping
- Wooden Queen Bee Excluder for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE 6 Frame Three Use Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- Metal Queen Bee Excluder for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the function of using a standardized queen excluder as a carrier? Improve Honeybee Protein Feeding Efficiency
- What are the advantages of using plastic queen excluders? Boost Apiary Efficiency and Pest Control
- How do queen excluders contribute to evaluating predatory mite impact? Standardize Research with HONESTBEE Equipment
- What is the significance of the physical barrier function provided by Queen Excluders? Boost Honey Purity & Efficiency
- What are the disadvantages of using a queen excluder? Maximize Your Hive Productivity and Colony Health



















