Target Readers: Commercial beekeepers, honey producers, and equipment distributors seeking reliable moisture management techniques to prevent spoilage and meet export standards.
Expectation Promise: This guide delivers proven strategies—from hive ventilation to post-harvest drying—backed by USDA/EU compliance benchmarks and real-world case studies.
The Critical Role of Moisture Control in Honey Processing
Why Moisture Content Determines Shelf Life and Market Value
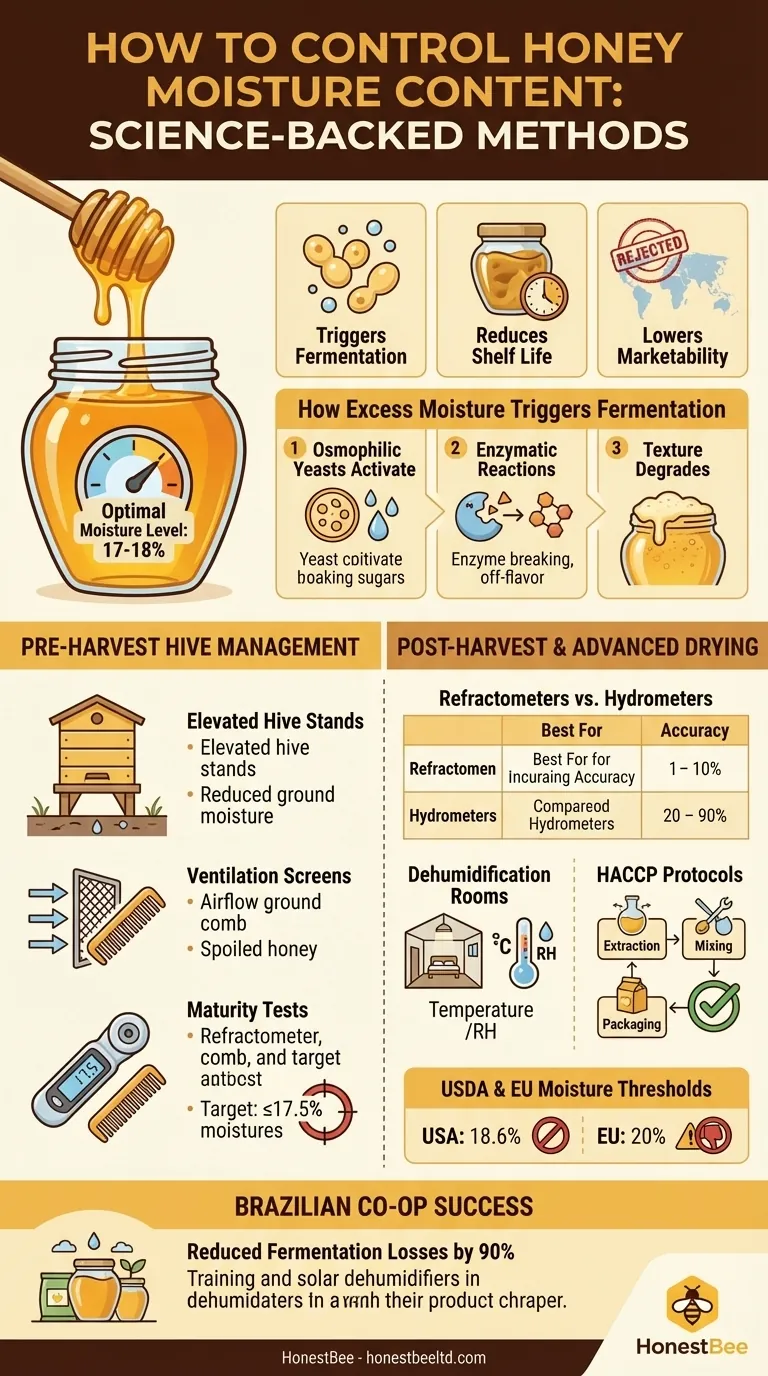
Honey’s longevity and quality hinge on maintaining optimal moisture levels (typically 17–18%). Research shows that exceeding 20% moisture:
- Triggers fermentation: Yeasts metabolize sugars, producing alcohol and carbon dioxide.
- Reduces shelf life: Microbial growth accelerates, causing spoilage within weeks.
- Lowers marketability: Export markets (e.g., EU, USA) reject honey above 18.6% moisture.
Key Insight: "Bee farming requires careful moisture management to prevent contamination," notes industry literature.
How Excess Moisture Triggers Fermentation: A Biochemical Perspective
When moisture surpasses 20%:
- Osmophilic yeasts (e.g., Zygosaccharomyces) activate, thriving in high-water-activity environments.
- Enzymatic reactions break down glucose/fructose, creating off-flavors and gas bubbles.
- Texture degrades—honey becomes frothy or overly runny.
Pro Tip: Harvest only when bees cap >80% of comb cells, signaling low moisture (<18%).
Industry-Approved Techniques for Moisture Management
Pre-Harvest Hive Management: Ventilation and Honey Maturity Checks
For high-humidity regions:
- Elevated hive stands: Raise hives 12–18 inches to reduce ground moisture absorption (studies show 5–8% lower internal humidity).
- Ventilation screens: Improve airflow between supers, discouraging condensation.
- Maturity tests: Use refractometers to spot-check uncapped honey (target: ≤17.5% before extraction).
Post-Harvest Tools: Refractometers vs. Hydrometers
| Tool | Best For | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Refractometer | Precise field testing | ±0.2% |
| Hydrometer | Bulk batch measurements | ±1% |
Cost-Saving Hack: Calibrate tools weekly with distilled water to maintain accuracy.
Advanced Drying Methods: Dehumidification and HACCP Protocols
- Dehumidification rooms: Maintain 35–40% RH at 80°F for 24–48 hours (reduces moisture by 2–3%).
- HACCP compliance: Document moisture levels at each stage—extraction, mixing, and packaging—to meet USDA audits.
Case Studies and Standards
Lessons from a Brazilian Honey Co-op’s Success
A cooperative in São Paulo reduced fermentation losses by 90% through:
- Training farmers to use refractometers before harvest.
- Installing solar-powered dehumidifiers in storage units.
USDA and EU Moisture Thresholds: Export Compliance
| Market | Max Moisture | Penalty |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 18.6% | Rejected batches |
| EU | 20% | Tariff increases up to 15% |
Global Tip: Blend high- and low-moisture honey to hit target ranges legally.
Ready to Optimize Your Honey Quality?
HONESTBEE’s beekeeping supplies—from precision refractometers to hive ventilation systems—help commercial apiaries maintain perfect moisture levels and pass export inspections. Explore our solutions today to protect your harvests and profits.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Honey Refractometer Instrument for Quality Assessment
- 8-Frame Electric Self-Reversing Honey Extractor Spinner for Commercial Honey Extraction Equipment
- HONESTBEE 3-Frame Manual Acrylic Honey Extractor
- Professional Thermostatic Conical Honey Melter
- Stainless Steel Manual Honey Press with Guard for Pressing Honey and Wax
Related Articles
- How Beekeepers Prevent Honey Spoilage Through Precision Moisture Control
- How to Accurately Test Honey Readiness: Science-Backed Methods for Beekeepers
- The Unseen Architecture of Trust: Calibrating the Honey Refractometer
- The Second Half of the Measurement: Protecting the Integrity of Your Honey Refractometer
- How to Perfect Honey Moisture Levels: A Beekeeper’s Guide to Refractometer Mastery




















