Beekeepers face unique challenges when selecting hive designs—extreme temperatures, difficult terrain, and accessibility constraints all impact colony health and honey production. This guide examines how to match hive types to environmental conditions, backed by real-world performance data and material science insights.
Choosing the Right Hive for Your Environment
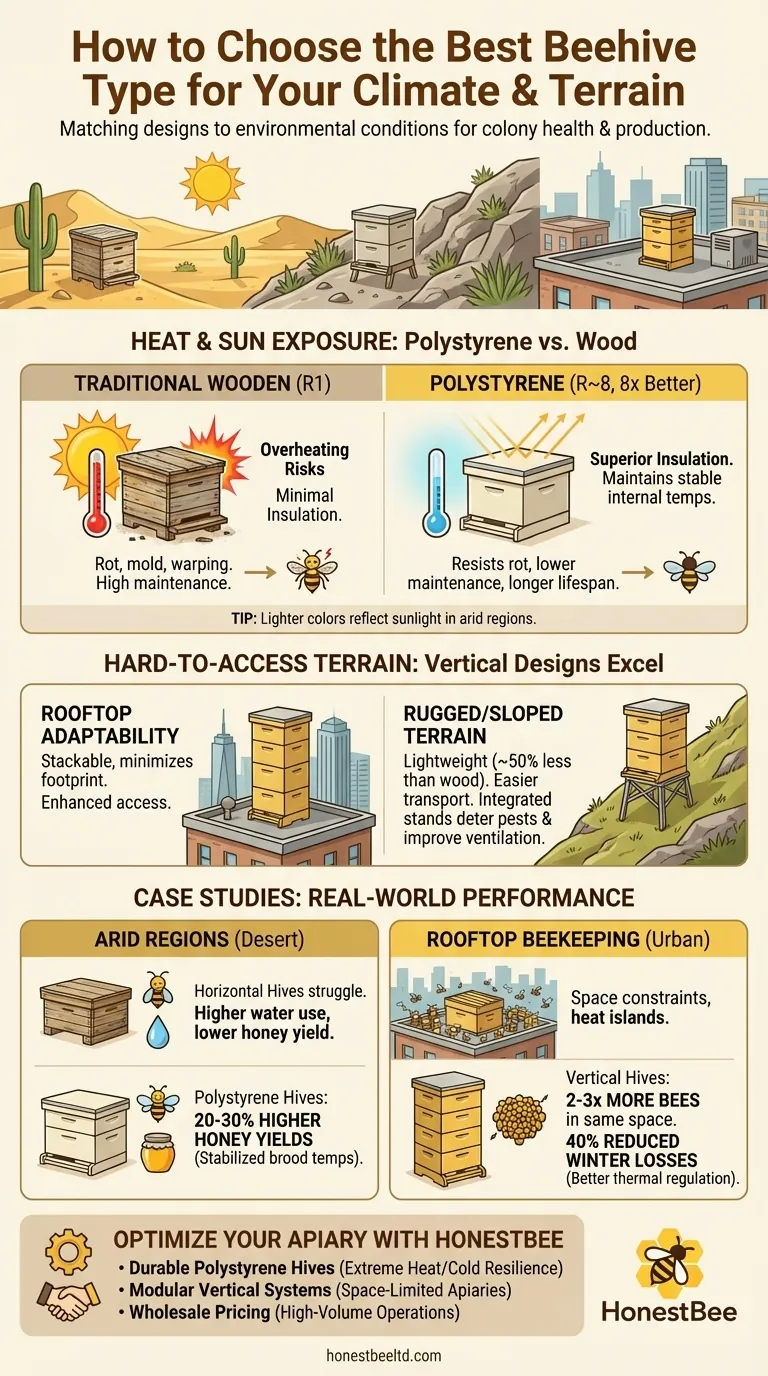
How Heat and Sun Exposure Impact Hive Durability
Beehives in hot climates need superior insulation to prevent overheating. Research shows polystyrene hives outperform traditional wooden designs by maintaining stable internal temperatures:
- 8x better insulation: High-density EPS (expanded polystyrene) provides an R-value of ~8 compared to wood’s R1, reducing temperature fluctuations that stress colonies.
- Longer lifespan: Unlike wood, polystyrene resists rot, mold, and warping, cutting long-term replacement costs.
- Lower maintenance: No painting or chemical treatments are needed, saving time for commercial beekeepers.
Practical tip: In arid regions, lighter-colored polystyrene hives reflect sunlight, further reducing heat absorption.
Managing Hives in Hard-to-Access Terrain
Vertical hive designs excel in urban or rugged environments:
- Rooftop adaptability: Stackable vertical hives minimize footprint while improving beekeeper access. Elevated stands enhance ventilation and deter ground pests.
- Lightweight advantage: Polystyrene hives weigh ~50% less than wooden equivalents, easing transport to remote sites.
Case in point: Apiaries on sloped terrain benefit from vertical setups with integrated stands, which reduce moisture buildup—a key factor in preventing hive diseases.
Case Studies: Hive Performance Across Climates
Arid Regions vs. Horizontal Hives
In desert climates, traditional horizontal Langstroth hives struggle with:
- Overheating risks: Thin wooden walls offer minimal insulation, forcing bees to expend energy cooling the hive instead of honey production.
- Higher water consumption: Colonies in poorly insulated hives require more water for evaporative cooling.
Solution: Beekeepers in Arizona and Saudi Arabia report 20–30% higher honey yields after switching to insulated polystyrene hives, thanks to stabilized brood temperatures.
Rooftop Beekeeping Success with Vertical Designs
Urban beekeepers face space constraints and heat islands. Vertical hives address both:
- Space efficiency: A single 5-layer vertical hive occupies the same space as one Langstroth box but houses 2–3x more bees.
- Thermal regulation: Stacked designs buffer against rooftop temperature swings.
Example: A Chicago rooftop apiary reduced winter colony losses by 40% after adopting vertical polystyrene hives with insulated covers.
Optimize Your Apiary with the Right Equipment
Matching hive design to your environment isn’t just about survival—it’s about maximizing productivity. HONESTBEE supports commercial beekeepers and distributors with durable, climate-adapted hive solutions:
- Polystyrene hives for extreme heat/cold resilience
- Modular vertical systems for space-limited apiaries
- Wholesale pricing for high-volume operations
Ready to upgrade your beekeeping setup? Explore HONESTBEE’s wholesale catalog for equipment designed to thrive in your specific conditions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Professional Dual-End Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- Professional Drop-Style Hive Handles for Beekeeping
Related Articles
- More Than Steel: How a Simple Hive Tool Dictates the Success of an Apiary
- More Than Steel: The Hive Tool as a Vector for Apiary Health
- Essential Beekeeping Equipment for Beginners: Functions, Selection, and Best Practices
- The Physics of Propolis: Why Your Hive Tool Choice Defines Your Apiary's Workflow
- Beyond the Scrape: A Beekeeper's Protocol for Preventing Invisible Catastrophe




















