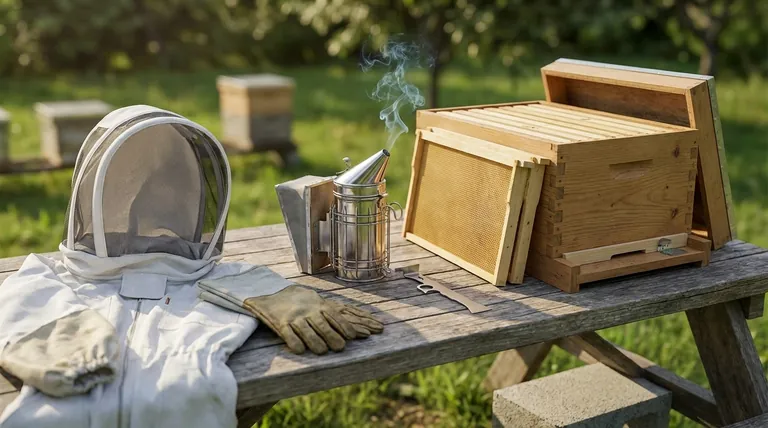
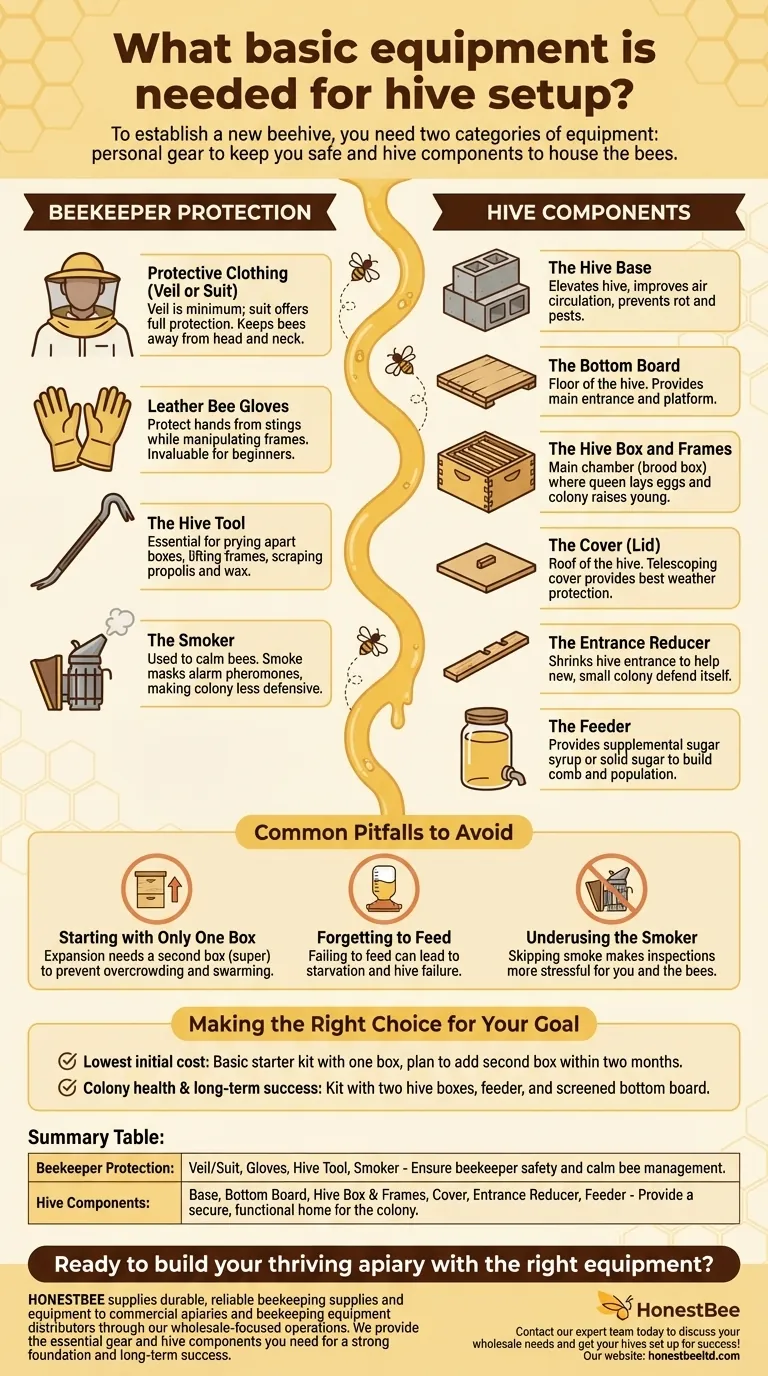
To establish a new beehive, you need two categories of equipment: personal gear to keep you safe and hive components to house the bees. The essential items include a protective veil or suit, gloves, a hive tool, and a smoker for yourself, along with a base, bottom board, hive box with frames, a cover, an entrance reducer, and a feeder for the colony.
A successful start in beekeeping depends on understanding that your equipment serves two distinct purposes: protecting you from the bees and providing the bees with a secure, functional home. Getting both parts right from the beginning is the foundation of a healthy hive.

Essential Gear for the Beekeeper
Before you can manage a hive, you must ensure your own safety and ability to work calmly. These tools are non-negotiable for hive inspections and maintenance.
Protective Clothing (Veil or Suit)
A veil is the absolute minimum protection required. It keeps bees away from your face, head, and neck, which are the most dangerous places to be stung. A full suit offers complete protection and is highly recommended for beginners to build confidence.
Leather Bee Gloves
Thick leather gloves protect your hands from stings while you manipulate frames. While they slightly reduce dexterity, they are invaluable for preventing painful stings that can make a new beekeeper hesitant and clumsy.
The Hive Tool
This is the beekeeper's crowbar. Bees seal every crack in their hive with a sticky resin called propolis. A hive tool is essential for prying apart hive boxes, lifting frames, and scraping away excess wax and propolis.
The Smoker
A smoker is used to calm the bees before and during an inspection. Puffs of cool, white smoke mask the alarm pheromones that guard bees release, making the colony less defensive and easier to manage.
Core Components of the Hive
This is the physical structure that your new colony will call home. Each component serves a specific and critical function.
The Hive Base
The base, often just a pair of concrete blocks or a dedicated stand, elevates the hive off the ground. This improves air circulation, prevents the bottom board from rotting, and discourages pests like ants from easily accessing the hive.
The Bottom Board
This component serves as the floor of the hive. It provides the main entrance for the bees and a platform for the rest of the hive components to be stacked upon.
The Hive Box and Frames
The hive box (or "brood box") is the main chamber of the hive. This is where the queen will lay her eggs and the colony will raise its young. Inside the box hang several frames (typically 8 or 10), which hold the wax comb for brood, pollen, and honey.
The Cover (Lid)
The cover acts as the roof of the hive. A telescoping cover, which overhangs the top hive box, is the most common type and provides the best protection from rain, sun, and other weather elements.
The Entrance Reducer
This is a small, simple piece of wood with different-sized notches cut into it. It is used to shrink the size of the hive entrance, which is critical for a new, small colony to defend itself against pests and robber bees from stronger hives.
The Feeder
A feeder is used to provide the colony with supplemental sugar syrup or solid sugar. This is crucial for helping a new package or nucleus colony draw out wax comb and build up its population, especially if there isn't a strong natural nectar flow.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding your equipment is only half the battle. Knowing how to use it correctly and when to expand on it is critical for your colony's survival.
Starting with Only One Box
While a new colony starts in a single hive box, it will expand rapidly. A common mistake is not being prepared with a second box (a "super") to add on top. Without this extra space, the colony can become overcrowded and may swarm (leave to find a new home).
Forgetting to Feed
A new colony expends enormous energy building wax comb. Failing to feed them consistently in the beginning, especially during periods of poor weather or low nectar, can lead to starvation and the complete failure of the hive.
Underusing the Smoker
Many beginners are hesitant to use the smoker, fearing it will harm the bees. In reality, a properly used smoker is a calming tool that prevents defensive behavior. Skipping this step makes inspections more stressful for both you and the bees.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your initial equipment purchase sets the stage for your first year. Your decision should be based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is the lowest initial cost: Purchase a basic starter kit with a single hive box, but have a plan and budget to buy a second box within the first two months.
- If your primary focus is colony health and long-term success: Invest in a kit that includes two hive boxes from the start, along with a feeder and a screened bottom board for better pest management.
Ultimately, the right equipment gives you the confidence to manage your bees effectively and provides the colony with the secure foundation it needs to thrive.
Summary Table:
| Category | Essential Items | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Beekeeper Protection | Veil/Suit, Gloves, Hive Tool, Smoker | Ensure beekeeper safety and calm bee management. |
| Hive Components | Base, Bottom Board, Hive Box & Frames, Cover, Entrance Reducer, Feeder | Provide a secure, functional home for the colony. |
Ready to build your thriving apiary with the right equipment?
HONESTBEE supplies durable, reliable beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors through our wholesale-focused operations. We provide the essential gear and hive components you need for a strong foundation and long-term success.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your wholesale needs and get your hives set up for success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional 3-Bar Frame Grip with Integrated Hive Tool
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Professional Pneumatic Wire Embedder for Beehive Frames
- Professional Engraved Round Hive Number Tags for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the hole in a hive tool for? A Multi-Tool for Apiary Repairs and Maintenance
- What are the basic tools for beekeeping? Essential Starter Kit for Safe & Successful Hive Management
- What is the function of a professional stainless steel hive tool in IFB? Optimize Your Colony Strength Assessment
- How does the hive splitting process contribute to colony management? Master Your Apiary Recovery Strategies
- What is the significance of professional hive-making tools? Scale Your Stingless Bee Farm with Precision Equipment



















