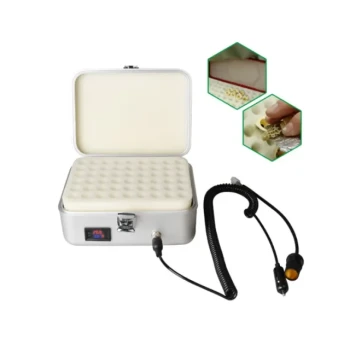
A -20 degree Celsius industrial-grade freezer serves as the critical stabilization point for bee pollen. By maintaining this specific low-temperature environment, the equipment effectively arrests enzymatic reactions and biological degradation that begin immediately after harvest. This ensures that the pollen's active ingredients and pigments remain chemically stable, protecting the sample's biological integrity from the moment of collection through to final laboratory analysis.
Bee pollen is a biologically active substance that rapidly degrades and oxidizes when exposed to ambient temperatures. Storage at -20°C locks in the sample's chemical profile, preventing spoilage and ensuring that research data or final products reflect the true quality of the original specimen.
The Mechanisms of Preservation
Inhibiting Enzymatic Reactions
Bee pollen is rich in active ingredients that are highly sensitive to their environment. Without deep freezing, natural enzymes within the pollen remain active, breaking down nutritional compounds.
A -20°C environment significantly slows or halts these metabolic processes. This preservation is essential for accurate research, as it prevents the chemical composition of the sample from changing before it can be analyzed.
Preventing Oxidation and Discoloration
Pollen contains delicate pigments and nutrients that are prone to oxidation. Exposure to fluctuating ambient temperatures causes these components to degrade, leading to visible discoloration and a loss of nutritional potency.
By maintaining a consistent deep-freeze, you protect these pigments from oxidative stress. This ensures the pollen retains its vibrant color, which is a key indicator of freshness and quality.
Controlling Lipid Stability
Beyond pigments, bee pollen contains lipids that can spoil or become rancid over time. The primary and supplementary data indicate that low-temperature storage inhibits lipid oxidation.
While dried pollen can be stored at slightly higher temperatures (around -12°C), a -20°C environment offers superior protection against lipid degradation, preserving the natural aroma and biological value of the material.
Integrity Across the Workflow
Consistency from Field to Lab
In a research context, the variable of greatest concern is often the time lag between sample collection and analysis. Any temperature fluctuation during this window introduces data errors.
Using an industrial-grade freezer eliminates this variable. It guarantees that the biological state of the pollen in the laboratory is identical to its state at the point of origin.
Commercial Product Quality
For production workflows, consumer perception relies heavily on sensory cues like smell and color. Degradation leads to a dull appearance and stale aroma.
Deep freezing acts as a quality control checkpoint. It ensures that the final processed product delivers the consistent sensory experience and nutritional benefits expected by consumers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of "Industrial-Grade" Stability
It is not enough to simply reach -20°C; the equipment must maintain it without fluctuation. Residential freezers often cycle temperatures (auto-defrost), which can temporarily thaw microscopic sections of the sample.
Fluctuation is the enemy. Even brief spikes in temperature can reactivate enzymes or accelerate oxidation. You must rely on industrial-grade units designed for tight temperature uniformity to guarantee the protection described above.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether you are conducting high-stakes research or managing a production line, the role of the freezer changes slightly based on your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is Research Accuracy: Prioritize -20°C storage to completely arrest enzymatic activity, ensuring your analytical data represents the pollen's original biological state.
- If your primary focus is Commercial Production: Focus on the freezer's ability to prevent oxidation, ensuring the visual color and aroma remain appealing for the final consumer.
A consistent -20°C environment is the only way to transform fragile, perishable bee pollen into a stable, reliable resource.
Summary Table:
| Preservation Mechanism | Impact on Bee Pollen | Importance for Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Enzymatic Inhibition | Halts metabolic processes & breakdown | Preserves active nutritional ingredients |
| Oxidation Control | Prevents discoloration & nutrient loss | Maintains vibrant color & freshness |
| Lipid Stability | Inhibits rancidity & spoilage | Protects natural aroma & biological value |
| Thermal Uniformity | Eliminates temperature fluctuations | Ensures data accuracy & sample consistency |
Secure Your Hive’s Harvest with HONESTBEE
Maximize the value of your bee products with the industry’s most reliable preservation solutions. HONESTBEE specializes in supporting commercial apiaries and distributors by providing a full spectrum of professional beekeeping tools, advanced machinery, and essential consumables.
Whether you need precise industrial-grade freezers to protect your pollen’s integrity, honey-filling machines to scale production, or specialized hive-making hardware, we deliver the quality and expertise required to thrive in the competitive honey market.
Ready to elevate your production workflow?
Contact HONESTBEE Today to explore our wholesale offerings and discover how our comprehensive equipment portfolio can enhance your business efficiency and product quality.
References
- Leandra Schuastz Breda, Maria Lurdes Felsner. SEASONAL VARIABILITY IN POLLEN COLORING OF Apis mellifera AND STINGLESS BEES. DOI: 10.22533/at.ed.9733132324082
This article is also based on technical information from HonestBee Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 30 cm Plastic Entrance Hole Bee Pollen Trap and Collector
- Plastic Bee Pollen Trap Strips Comb Catcher Collector
- Heavy Duty Stainless Steel Queen Bee Catcher Clip
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- Yellow Plastic Bucket Pail Perch for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-performance pollen trap? Maximize Yield and Purity in Your Apiary
- Why is specialized pollen drying equipment necessary for processing bee pollen? Ensure Safety & Nutrient Preservation
- How do front-mounted pollen traps facilitate the collection of pollen balls? Efficient Tools for Pure Pollen Harvesting
- What role does a centrifuge play in the acetolysis method? Enhance Pollen Isolation and Botanical Identification
- What is the function of a pollen trap for colony monitoring? Transform Your Hive Into a Precision Environmental Biosensor
- What role do specialized pollen traps and royal jelly tools play in diversifying commercial apiary revenue streams?
- What are some methods to preserve collected pollen? Freeze, Dry, or Mix with Honey
- Why is it necessary to equip commercial bee hives with specialized pollen traps? Maximize Purity & Harvesting Efficiency